文章导读
2020年9月 第一期
学者简介
研究方向及意义
目前研究重点
未来研究关注重点
近五年发表的论文
01
学者简介

张一新 教授、博士生导师,现任苏州大学建筑学院风景园林系特聘教授、环境保护与生态修复技术研究中心主任,香港大学浙江科学技术研究院特聘研究员,及西安交通大学2020“国际一流学者讲学计划”讲学教授;并担任中国建筑文化研究会生态人居及康养专委会副主任及专家委员会主任、中国城市科学研究会景观学与美丽中国建设专业委员会委员、中国生态学学会可持续生态专业委员会委员和流域生态学专业委员会委员,国际SCI期刊编委Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems(JCR海洋&淡水生物学 一区),国际SCI期刊 Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution (JCR环境科学&生态学 二区)客座编辑Guest Editor。发表论文70余篇。
02
研究方向及意义
研究方向重点在河流生态学(Stream and River Ecology)、滨岸带生态学(Riparian Ecology)、和修复生态学(Restoration Ecology)。长期致力于环境变化对水生生物个体、种群及群落的生态学过程以及生态系统功能影响机制的研究。在河流与河岸带的小尺度野外生态实验研究侧重于水生生物功能形态、表型塑性变化、消费者取食模式的转换以及入侵种与本地种相互作用对生态系统功能的影响;流域大尺度生态系统研究着重于流域范围土地利用变化(如城镇化过程,森林砍伐),及人类活动干扰(如气候变暖,PM2.5, 农药,微塑料) 对生物个体行为、生物多样性及生态系统功能的影响,以及跨水域-陆地生态系统的资源补充营养流的生态学作用及效应。通过从个体生态学、种群生态学、群落生态学和生态系统生态学多视角多层次对河流与河岸带生态系统做深入及系统的研究探索,为城市与农村所急需的生态修复实践与应用提供理论基础,有助于流域生态系统的修复以及可持续的流域生态系统管理体系建立。
03
目前研究重点
跨溪流生态系统(Stream Ecosystem)-陆地滨岸带生态系统(Riparian Ecosystem)的物质-营养-能量资源补贴流(Subsidy flux)的生态系统效应及生态学作用机制。
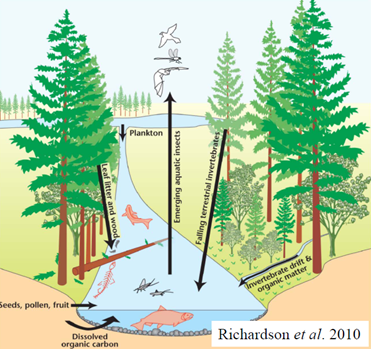
Science Advances: 全球尺度解析河流-河滨生态系统的功能模式及其驱动因素。
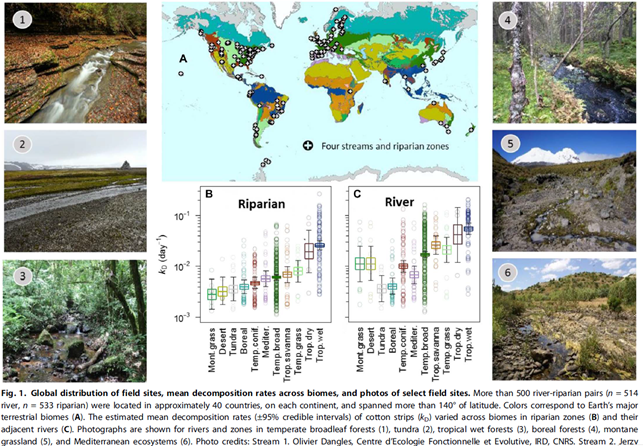
本项目有世界各地150多个研究组参与。科学问题是:河流生态系统的功能模式在全球尺度上是怎样的?河流生态系统碳代谢速率随纬度变化呈现何种趋势?首次在大尺度上系统解析了河流功能随纬度的变化趋势,初步分析了影响功能模式的驱动因素。纬度越高的地带,温度对降解速率的制约越明显;而纬度越低的地带,其他因素对降解速率的制约越发凸显,如营养盐的影响等。
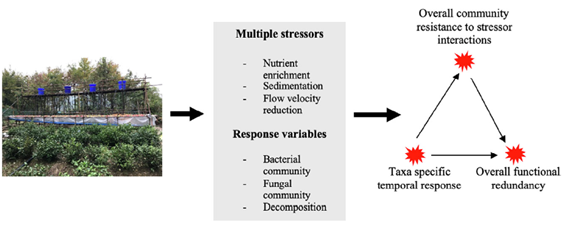
关注日益增强的人类活动产生的多重环境胁迫,导致的河流湖泊湿地及滨岸带生态系统的生境质量退化和联通性受损及生物多样性减少和生态系统功能丧失的效应与机制。通过高度可重复的野外河流微宇宙(Exstream System: 64个实验单位), 研究多个环境胁迫因子,如细沉积物、流速、营养盐、水位变化、生境结构、实验时间,对有机凋落物分解和底栖生物膜相关的微生物群落及底栖无脊椎动物群落的的影响机制,推断不同群落的结构和功能特性。
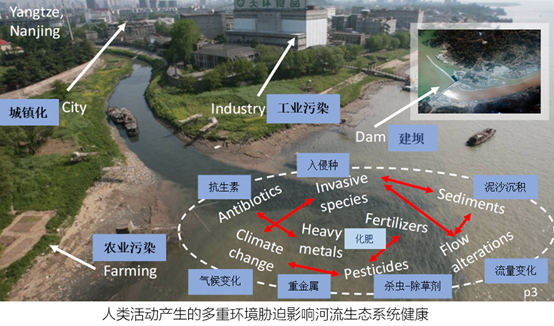
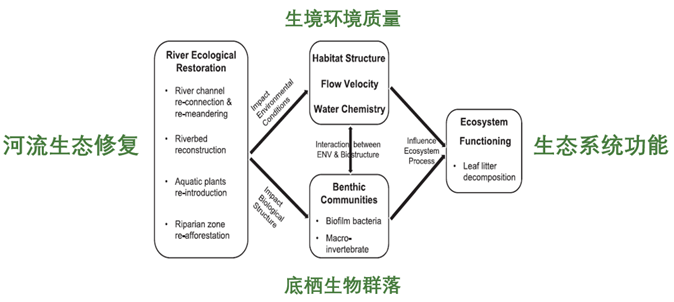
基于生物多样性恢复与提升的河流生态系统的生境修复与流域的生态系统功能修复。
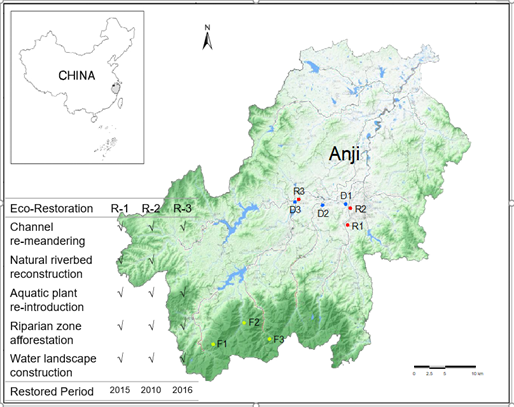
通过对不同类型河流生态系统(Forest river, Urban degraded river, Urban restored river)的比较研究, 探索有机凋落物分解(Organic matter breakdown)和底栖生物膜(Benthic biofilm)相关的微生物群落及底栖无脊椎动物群落对河流生态修复的生态学响应机制。
04
未来研究关注重点
基于生态系统服务的河湖湿地水域网络连通提升与优化生态设计
水域-滨岸带生态健康修复的景观生态与生物多样性规划与设计途径
生态-人居-康养的可持续动态耦合与演化模式
突发环境事件下区域环境生态韧性作用与演变机制
05
近期发表的文献
7. Huang,Q., Lin, Y. Y., Zhong, Q. Y., Ma, F., Zhang, Y. X.* 2020. Impacts of microplastic particles on predator-prey population dynamics:The implication of Lotka-Volterra model. Scientific Reports, 10:4500.
8. Juvigny-Khenafou, N. P. D., Zhang,Y. X.*, Piggott, J. J., Atkinson, D.,Matthaei, C. D., Van Bael, S. A., Wu, N. C. 2020. Anthropogenic stressorsaffect fungal more than bacterial communities in decaying leaf litter: a stream mesocosm experiment. Scienceof the Total Environment 716 (2020) 135053.